
NBMA is a network type used in the OSPF communications protocol, which unlike the Border Gateway Protocol is primarily used for the LAN and data center. OSPF Network Types Broadcast-A network type that connects two or more OSPF routers over a broadcast media such as Ethernet or FDDI. NBMA networks will often use next hop resolution protocol to find routes through the network automatically. Because of this, routing information must be shared between nodes. Ethernet is commonly multiple access.Īn NBMA host must be able to communicate directly with all other hosts on the network, but the hosts may not be directly connected on the same physical link. OSPF assumes that all non-broadcast networks are multiple access. This contrasts with single access or point-to-point networks where each interface on a host only connects to a single other host. Multiple access in NBMA means that a single physical link or interface can communicate with multiple hosts. On a broadcast network, all hosts receive and check all packets sent on the network, so a broadcast message to all is simply a single packet that is addressed so all hosts should read it. To send a broadcast message to all hosts on a non-broadcast network, a separate packet addressed to each host must be sent. Switched networks or virtual circuits are used to provide direct routing of data packets. This contrasts with broadcast or multicast networks where each packet is received by all hosts on the network but is only read by its intended recipients. Non-broadcast in NBMA means that each data packet is only sent to one destination host.
#Ospf network types password#
0 implies no password, 1 implies the plain text password and 2 implies the MD5 authentication. 1.5 OSPF Network Types OSPF networks can implement in four different types as Broadcast (None Broadcast Multi Access ).
#Ospf network types 32 bit#
Area ID is the 32 bit area ID assigned to an interface sending an OSPF packet. The format of the common OSPF header is shown below. The other OSPF network types are broadcast, point-to-point and point-to-multipoint. In the OSPF, there are 5 different types of packets. It is used in X.25, frame relay, asynchronous transfer mode and powerline networking. Virtual circuits or switched network fabrics provide the direct communication. In an NBMA network all hosts are connected on a single network, but data is sent from one host directly to the next host and is not broadcast across to all hosts. The network type of Ethernet interfaces is broadcast. By default, the network type of an interface is determined by the physical interface. As a network engineer working with OSPF, you must understand the differences between each OSPF network type and their compatibility. In this article, we are going to discuss the two major network types, which are Point-to-Point and Broadcast. The undo ospf network-type command restores the default network type of the OSPF interface. OSPF Network Types Point-to-Point and Broadcast RFC 2328: OSPF Version 2 defines OSPF network types.
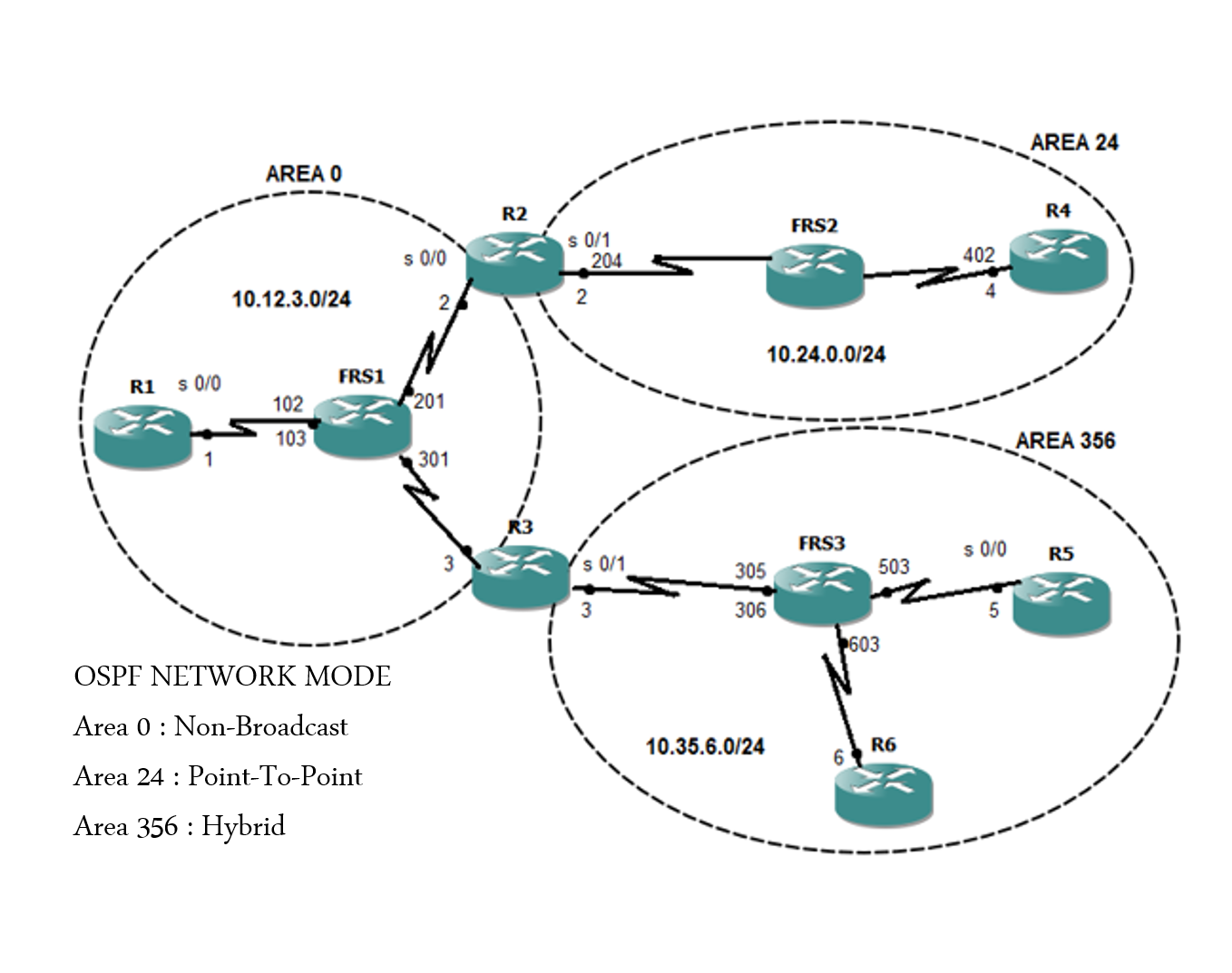
TL&DR: The current implementation of external routes in OSPF minimizes topology database size (memory utilization) Before going to the details, try to imagine the environment in which. Non-broadcast multiple access (NBMA) is one of four network types in the Open Shortest Path First ( OSPF) communications protocol. Function The ospf network-type command sets a network type for an OSPF interface. If ABR were able to change the Advertising Router ID in the Type-5 LSA, then there would be no need for Type-4 LSA which meant less OSPF overhead on the network. This might be necessary when dynamic circuits are in use.What is non-broadcast multiple access (NBMA)?

The non-broadcast parameter can be appended to the OSPF network type to force unicasting of packets rather than relying on multicast. All routers attached to a non-broadcast network must be manually configured to recognize it as a point-to-multipoint segment: Router(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-multipoint Hello packets must still be replicated and transmitted individually to each neighbor, but the multipoint approach offers two distinct advantages: no DR/BDR is needed, and the emulated point-to-point links can occupy a common subnet. Rather than trying to emulate broadcast capability, it seeks to organize the PVCs into a collection of point-to-point networks.
#Ospf network types how to#
Flip to see how to configure a router's interface priority to make the router the DR. Highest OSPF Router ID: If the priority ties, the election chooses the router with the highest OSPF RID. Point-to-Multipoint: A point-to-multipoint configuration approaches the non-broadcast limitation in a different manner. The better router will not become DR until the DR and BDR fails.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
